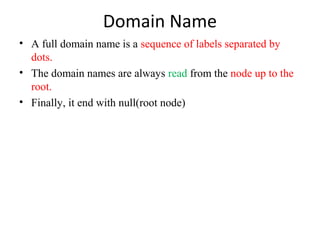
39 a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by
In domain name, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by ... In domain name, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A. dots B. colons C. semicolons D. question marks Answer: A 6 A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A semicolons ... 6 A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A semicolons B dots C from COMPUTER NETWORKS at Bandung State Polytechnic. Study Resources. Main Menu; by School; ... 6 A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A semicolons B dots C. 6 a full domain name is a sequence of labels.
A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated View full document. See Page 1. 6 : A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by ________. b. dots. 7 : If a label is terminated by a null string, it is called a __________. b. FQDN. b. FQDN 8 : If a label is not terminated by a null string, it is called a __________. located on a remote machine, he or she performs ___________ login.

A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by
RFC 1035: Domain names - implementation and specification RFC 1035 Domain Implementation and Specification November 1987 from master files stored locally or in another name server. The second kind of data is cached data which was acquired by a local resolver. This data may be incomplete, but improves the performance of the retrieval process when non-local data is repeatedly accessed. Data Communication and Networking - Domain Name System MCQs - ExamRadar Domain Name System multiple choice questions and answers MCQs . 1. What a server is responsible for or has authority over is called a _____. ... A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. semicolons; dots; colons; none of the above; 25. If a label is terminated by a null string, it is called a _____. ... label; name; domain ... In Domain Name, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by ... In Domain Name, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A. Dots B. Colons C. Semicolons D. Question marks The domain names are always read from the A. Node up to the root B. Node down to the leaf C. Root to Child D. All of them A root server usually does not store any information about domains but delegates its authority to the ...
A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by. Computer Network MCQ - DNS - Part 4 - StackHowTo A full domain name always ends with _____. A 1 nœud. B 2 nœuds. C 0 nœud. D Null nœud. Answer. D . Each node in the tree has a domain name. A complete domain name is a sequence of labels separated by dots (.). Domain names are always read from the node to the root. The last label is the root label (null). This means that a complete domain ... A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by Homechevron_rightEngineeringchevron_rightComputer Sciencechevron_rightData Communication and Computer Networkchevron_rightA full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by ________. STIX™ Version 2.1 26.07.2019 · 1 Introduction. Structured Threat Information Expression (STIX™) is a language and serialization format used to exchange cyber threat intelligence (CTI). STIX enables organizations to share CTI with one another in a consistent and machine-readable manner, allowing security communities to better understand what computer-based attacks they are most likely to see … HTML Standard Vor 2 Tagen · An encoding has an encoding name and one or more encoding labels, referred to as the encoding's name and labels in the Encoding standard. 2.1.8 Conformance classes. This specification describes the conformance criteria for user agents (relevant to implementers) and documents (relevant to authors and authoring tool implementers).
A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by Get the answers you need, now! gagan1355 gagan1355 22.05.2018 Computer Science Secondary School answered A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by 1 See answer Advertisement Advertisement A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by? A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by? In how many modes does DHCP allocate IP addresses to the network devices? Find how many types of servers does DNS define? Resolution of the IP address in which the client may send its request to multiple servers before getting an answer? Each domain name (each node on the tree) is ... Domain Network Services - Networking test Domain Network Services - Networking test. 1) Find how many types of servers does DNS define? A) 3. B) 4. C) 2. D) 1. View Answer / Hide Answer. 2) A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by? A) comma. In domain name, sequence of labels are separated by ______. - Computer ... In domain name, sequence of labels are separated by _____. - Computer Applications. Advertisement Remove all ads. ... My Profile [view full profile] why create a profile on Shaalaa.com? 1. Inform you about time table of exam. 2. Inform you about new question papers. 3. New video tutorials information.
A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. semicolons dots colons none of the above. Networking Objective type Questions and Answers. A directory of Objective Type Questions covering all the Computer Science subjects. SPARQL 1.1 Query Language - W3 1.2.4 Terminology. The SPARQL language includes IRIs, a subset of RDF URI References that omits spaces. Note that all IRIs in SPARQL queries are absolute; they may or may not include a fragment identifier [RFC3987, section 3.1].IRIs include URIs [] and URLs.The abbreviated forms (relative IRIs and prefixed names) in the SPARQL syntax are resolved to produce absolute IRIs. ImageMagick – Command-line Options Resize the image using data-dependent triangulation. See Image Geometry for complete details about the geometry argument. The -adaptive-resize option defaults to data-dependent triangulation. Use the -filter to choose a different resampling algorithm. Offsets, if present in the geometry string, are ignored, and the -gravity option has no effect. RFC 1034: Domain names - concepts and facilities - RFC Editor RFC 1034 Domain Concepts and Facilities November 1987 The domain system assumes that all data originates in master files scattered through the hosts that use the domain system. These master files are updated by local system administrators. Master files are text files that are read by a local name server, and hence become available through the name servers to users of the …
Domain Name System - Wikipedia The Domain Name System (DNS) is the hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to identify computers reachable through the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. The resource records contained in the DNS associate domain names with other forms of information. These are most commonly used to map human-friendly domain names to the numerical IP …
DNS (Domain Name System) | Networking Quiz - Quizizz In the domain name space, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. answer choices . Colon. Dot. Semicolon. None. Tags: Question 6 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. In the domain name space, if a label is terminated by a null string, it is called a _____.
RFC 1035 - Domain names - implementation and specification RFC 1035 Domain Implementation and Specification November 1987 from master files stored locally or in another name server. The second kind of data is cached data which was acquired by a local resolver. This data may be incomplete, but improves the performance of the retrieval process when non-local data is repeatedly accessed.
GitHub Flavored Markdown Spec Normally the > that begins a block quote may be followed optionally by a space, which is not considered part of the content. In the following case > is followed by a tab, which is treated as if it were expanded into three spaces. Since one of these spaces is considered part of the delimiter, foo is considered to be indented six spaces inside the block quote context, so we get an …
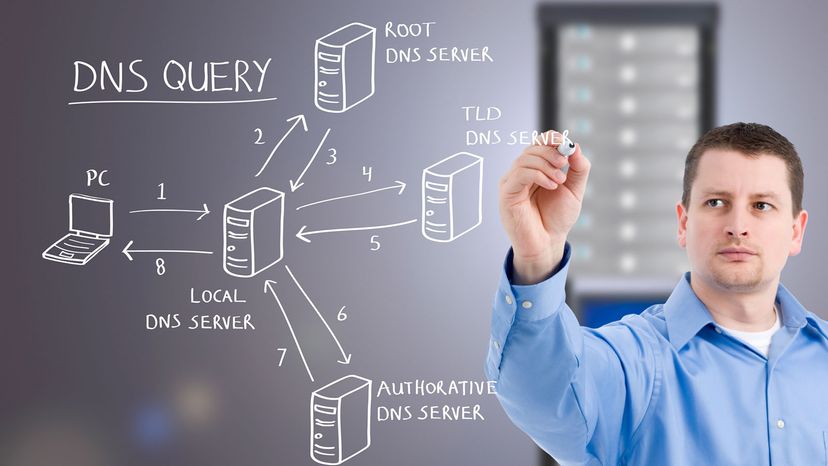
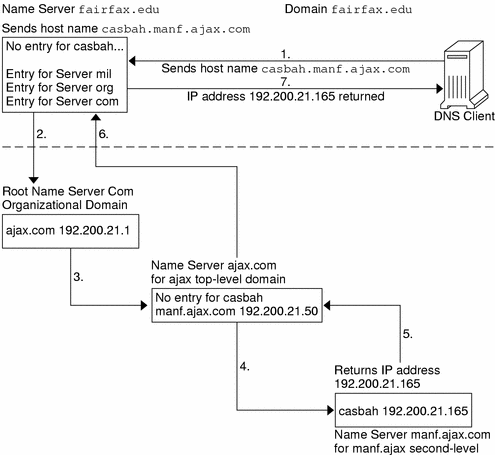
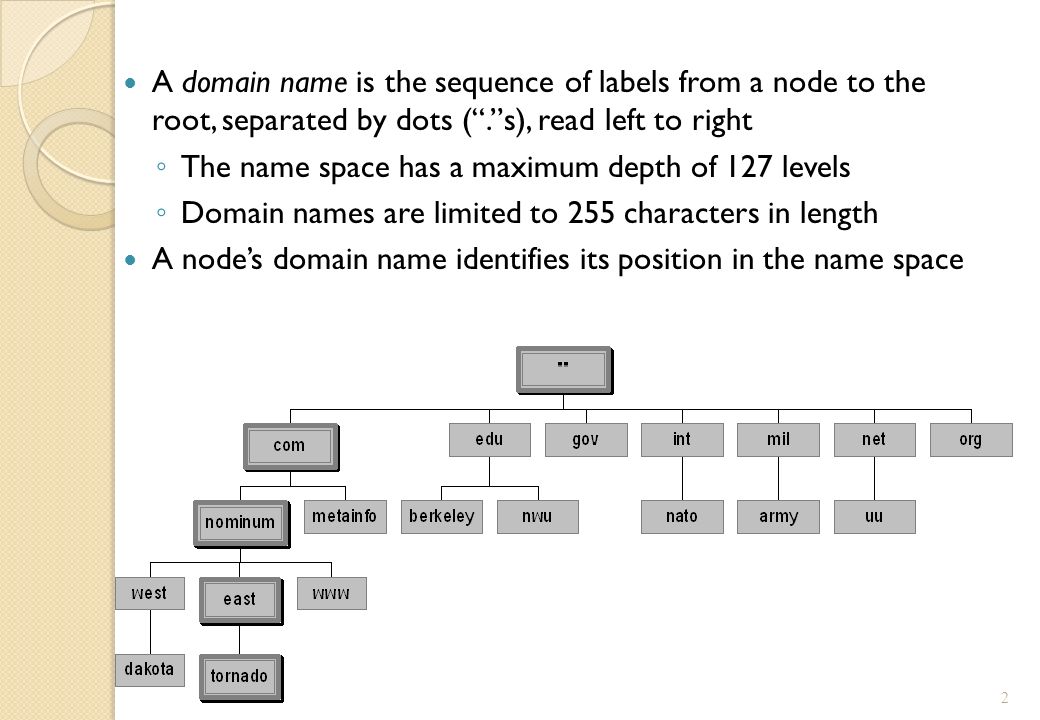
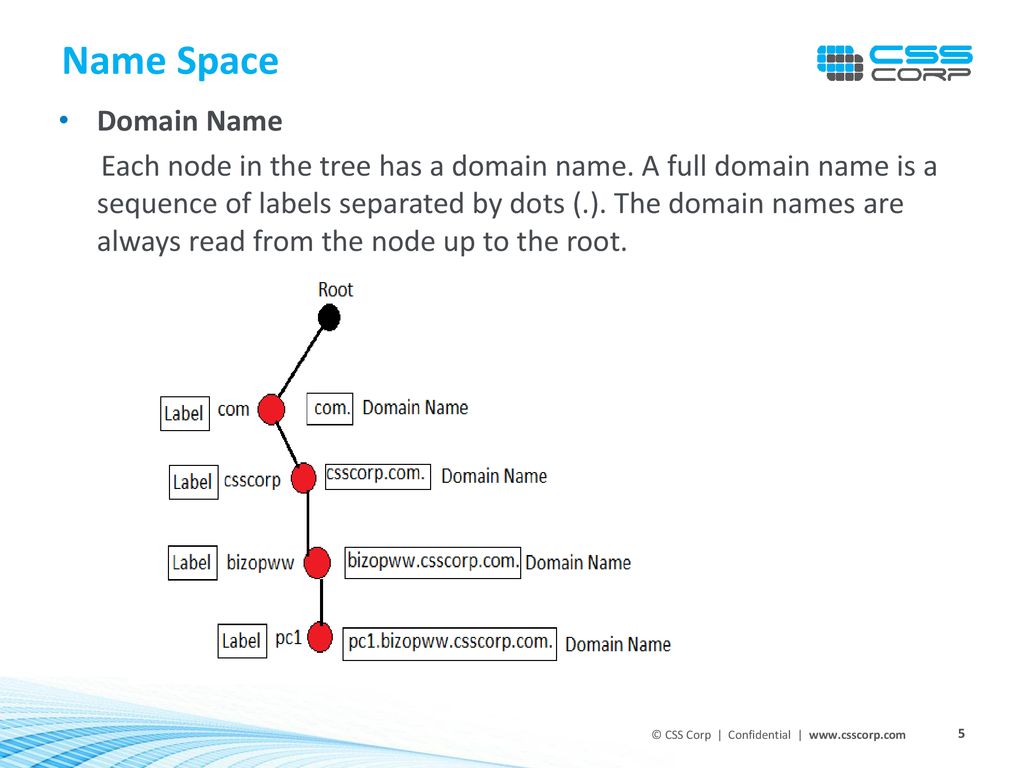
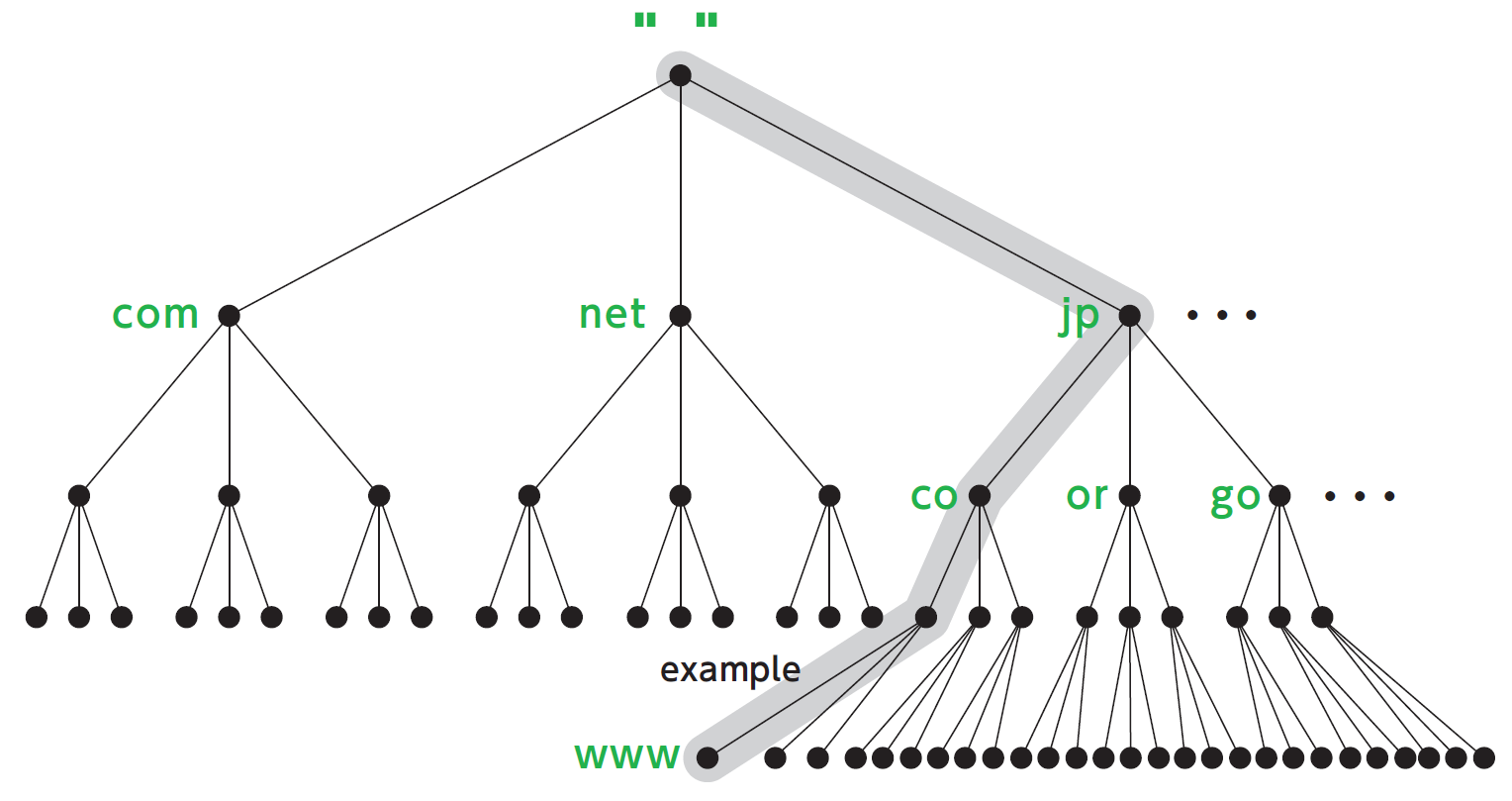
PDF DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) - IDC-Online full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by dots (.). The domain names are always read from the node up to the root. The last label is the label of the root (null). This means that a full domain name always ends in a null label, which means the last character is a dot because the null string is nothing. Figure shows some domain names.
Test 5 Flashcards & Practice Test | Quizlet A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. dots. ... In a URL, an optional _____ can be inserted between the host and the path, and it is separated from the host by a colon. none of the above. In a URL, the _____ is the computer on which the information is located.
75 Networking Interview Questions and Answers A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by dots (.). The domain names are always read from the node up to the root. Fully Qualified Domain Name If a label is terminated by a null string or empty string, it is called a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). Partially Qualified Domain Name If a label is not terminated by a null string ...
In domain name, sequence of labels are separated by In domain name, sequence of labels are separated by (a) ; (b) .(dot) (c) : (d) NULL
Empty string - Wikipedia Formally, a string is a finite, ordered sequence of characters such as letters, digits or spaces. The empty string is the special case where the sequence has length zero, so there are no symbols in the string. There is only one empty string, because two strings are only different if they have different lengths or a different sequence of symbols.
If a label is terminated by a null string, it is called a A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. Which of the following devices translates hostnames into IP addresses? When the secondary downloads information from the primary, it is called ______ transfer.
In Domain Name, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by ... In Domain Name, a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by A. Dots B. Colons C. Semicolons D. Question marks The domain names are always read from the A. Node up to the root B. Node down to the leaf C. Root to Child D. All of them A root server usually does not store any information about domains but delegates its authority to the ...
Data Communication and Networking - Domain Name System MCQs - ExamRadar Domain Name System multiple choice questions and answers MCQs . 1. What a server is responsible for or has authority over is called a _____. ... A full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by _____. semicolons; dots; colons; none of the above; 25. If a label is terminated by a null string, it is called a _____. ... label; name; domain ...
RFC 1035: Domain names - implementation and specification RFC 1035 Domain Implementation and Specification November 1987 from master files stored locally or in another name server. The second kind of data is cached data which was acquired by a local resolver. This data may be incomplete, but improves the performance of the retrieval process when non-local data is repeatedly accessed.
















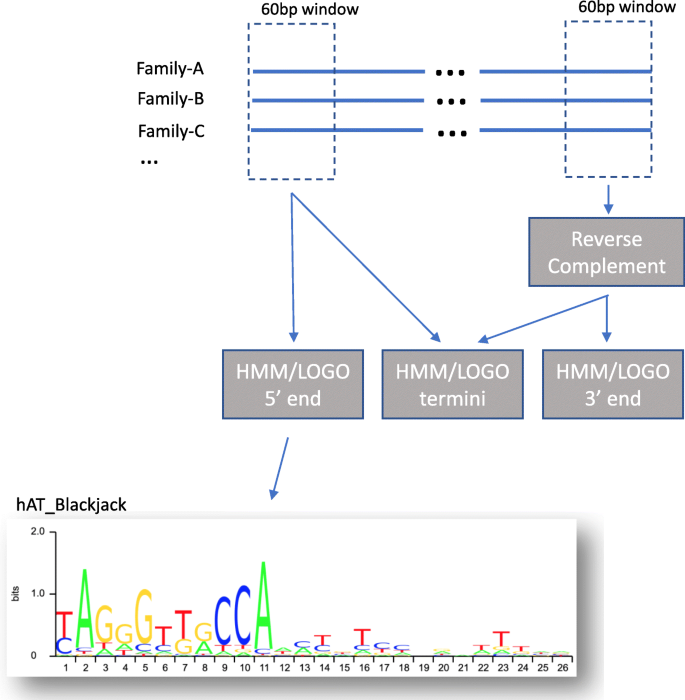
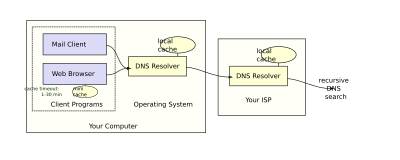
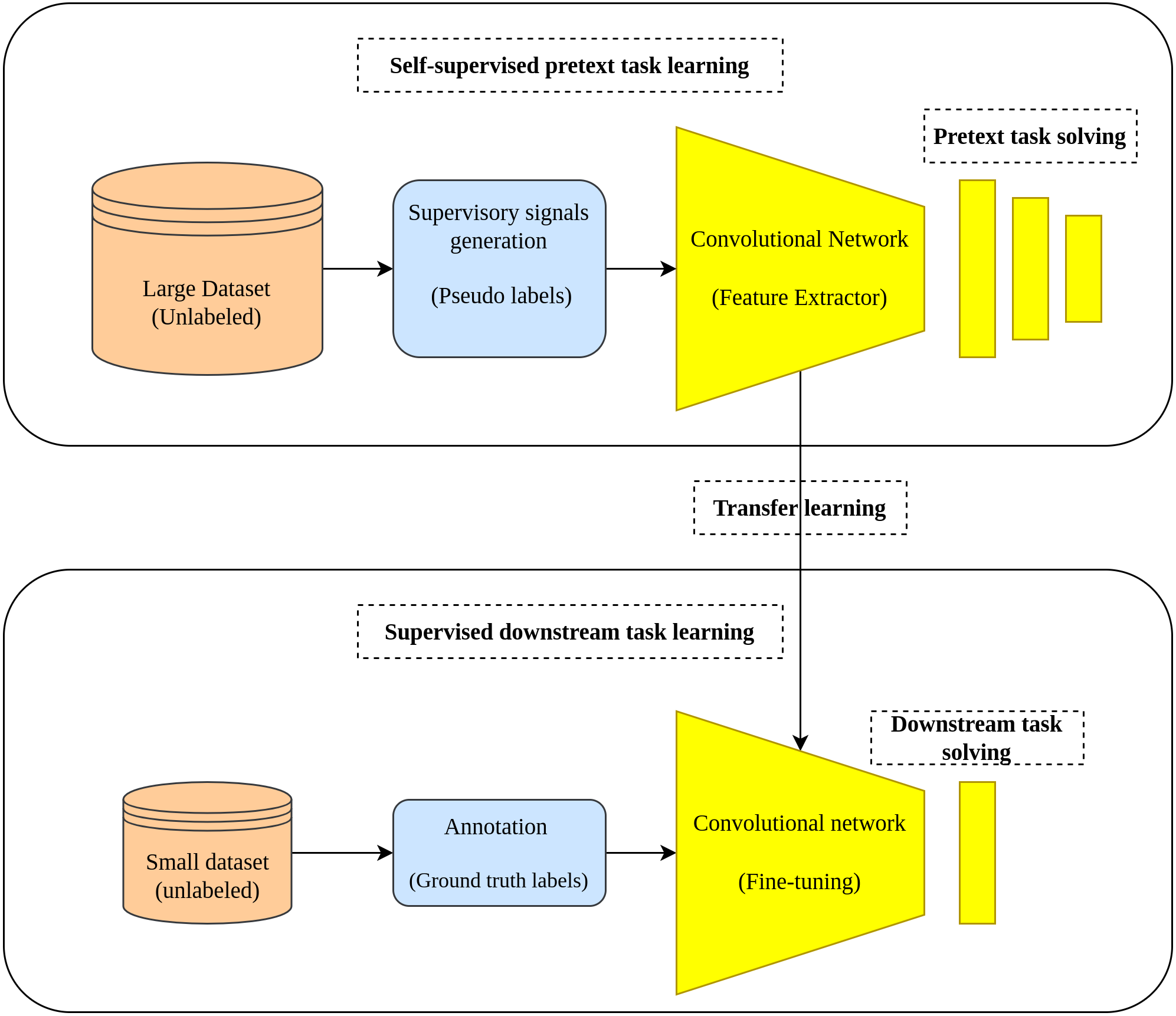
Post a Comment for "39 a full domain name is a sequence of labels separated by"